Engine Timing
Overview
Engine Timing Explained
Most engines have one crankshaft, one or more camshafts, and a timing chain (or a timing belt) that connects them.
Crankshaft moves pistons up and down the cylinder. Camshaft opens and closes intake and exhaust valves. These valve openings and closings have to be timed very precisely according to a corresponding piston position.
- That’s called Valve Timing.
Valve timing in a 4-stroke engine consists of the following strokes in each cycle:
- Intake stroke (intake valve open, to let the outside air in)
- Compression stroke (air gets compressed)
- Power stroke (all valves are closed, spark ignites the compressed air/fuel mixture)
- Exhaust stroke (exhaust valve opens to let the exhaust gases out)

When the engine is cranking, ECM constantly receives the crankshaft and camshafts angles of rotation (via CKP and CMP sensors, read below).
- If crankshaft and camshaft positions are synched (timing is correct), then ECM is able to calculate which cylinder is on the compression stroke (pre-spark stage), to start calculating when it will receive a spark.
- Note: Delivering a spark always at the same time (relative to corresponding piston position) is not optimal for fuel efficiency, power/torque efficiency, or emissions efficiency. Therefore ECM takes those aspects into consideration (along with engine rpm, engine load, drive mode settings, etc.) when it calculates the optimal time for delivering a spark.
-
Spark Advance vs Spark Retardation
- Let’s say the spark timing is 40 degrees BTDC (before top dead center) for producing optimum torque.
- Delivering a spark earlier than that is advancing it and delivering it after that is retarding it.
- Higher RPM ⇢ spark retardation to avoid knocking or detonation.
- If the spark timing is too advanced for that particular operating point, for that particular fuel (octane number, mixtures …), the peak temperature and pressure get so high, that the air/fuel mixture combusts before spark gets delivered. The solution to this is retarding spark. As soon as the knock sensor detects a shock, it retards the spark, thereby phasing the combustion to a later part of the engine cycle and hence, reducing the peak temperature and pressure and avoiding any further knock.
-
- That’s called Ignition Timing.
- Injector Timing (time at which the fuel injector opens and closes) uses mostly the same underlying principles as the ignition timing, so we will not discuss it here.
CKP & CMP Sensors
CKP Sensor (Crankshaft Position Sensor)
- CKP measures the rotation of a crankshaft.
- Just like there is only one crankshaft, so there is only one CKP Sensor.
- In a 4-stroke engine, 2 crankshaft rotations (720 degrees) = 1 camshaft rotation (360 degrees).
- CKP Sensor is the main input for the ECM to calculate ignition timing and injector timing.
- Without it car will not start.
- In addition, ECM uses CKP Sensor input for misfire detection.
- When cylinder misfires, engine slows down for a fraction of a second which is enough for CKP signal (see waveform example below) to send a bit longer pulse than usual. Duration of that pulse and it’s location on the waveform helps ECM to detect misfire event and calculate which cylinder has misfired.
CMP (Camshaft Position Sensor)
- Measures the rotation of a camshaft.
- Car usually has 1 CMP per camshaft; so with 4 camshafts there will be 2 Exhaust CMP Sensors and 2 Intake CMP Sensors.
CKP/CMP can be
- Inductive (2 wires). More Info.
- Hall Effect (3 wires). More Info.
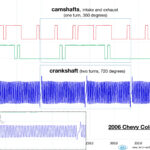
Here is a waveform example of the two CMP and CKP sensor signals. Notice how patterns repeat every 360 degrees of camshaft rotation
Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with VVL (variable valve lift) systems.
Exhaust VVT
- Later exhaust valve closure = bigger air/fuel mixture gulp = maximum engine power
- Sooner exhaust valve closure = smaller air/fuel mixture gulp = like having smaller engine = better mpg
More Info
- Read Variable Camshaft Timing/ Variable Valve Timing (by Matt Dixon from OpenSIUC)
Variable Valve Lift (VVL)
VVL is an automotive piston engine technology which varies the height a valve opens in order to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions.
Timing Troubleshooting
Testing
Method 1
- Use an Oscilloscope.
- Scope CKP and CMP sensors.
- Compare the waveform with a known good one (usually from a service manual).
- Example waveform
Method 2
- Use an Oscilloscope, Ignition Pickup Probe (e.g. COP or secondary ignition probe), and Pressure Transducer (e.g. WPS500X).
- Waveform will show where spark occurs in relation to a compression stroke.
- Spark should align close to the tip of compression stroke. If it is shifted, timing is off (good demonstration). 💡
Incorrect CMP/CKP signal
-
Gap between CMP/CKP sensor and reluctor is too big
-
Bad Reluctor
-
Bad CMP/CKP sensor
- Codes
- P0336 Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance
- P0340 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- 🩺 Intermittent No-Start | Bad CMP | 2004 Hyundai Santa Fe
- Codes
-
Wiring Issue
-
ECM
Incorrect CMP/CKP Correlation
-
Codes
- P0016 Crankshaft Position- Camshaft Position Correlation (Bank 1)
- P0017 Crankshaft Position- Camshaft Position Correlation (Bank 2)
- P0336 CKP sensor range/performance
- P0341 Camshaft Position Sensor (G40): Implausible signal
- 📝 Note that the ECM might not give a code when the timing is off (e.g. 2014 Ford Focus).
VVT/ VVL System
Valvetronic | BMW
- 📚 Valvetronic N55 OEM Manual
- 📎 No Start, 2DE3 & 36FD | Bad DME | 2012 335i (E92) with N55
- Recalibrating Servo Motor
- Use scantool to recalibrate Valvetronic Limit Stops
- Or try to
- Remove the servo motor.
- With a screwdriver push the eccentric shaft gear as far back counter clockwise as it can go.
- Insert the servo motor and connect its 2 pin plug.
- Switch the ignition onto position 2 and within 15 seconds depress the accelerator pedal down to full throttle 10 times and you will hear the servo motor program itself back to factory spec.
- Dirty Oil Filter, Dirty Oil, Not Enough Oil.
- Weak Oil pump
- VVT Solenoid Issue
-
📝 Misfire, P0016 | Bad VVT Solenoid | 11′ Subaru Outback
- P0016. Car ran very roughly with multiple misfires. Short fuel trim for one of the banks (don’t remember which one) went +30%, another was -30%. One O2 was very rich and another was very lean, with no fluctuations. VVT advance for Bank 1 in DATA was 44 degrees, with OCV Duty Bank 1 (command for VVT) 0%. VVT advance for Bank 2 in DATA was 0 degrees, with OCV Duty Bank 2 (command for VVT) 0%. After swapping VVT solenoid, a problem appeared on the different side. Turns out, VVT solenoid for Bank 1 was a little bent and thus was stuck open.
-
- VVT Actuator
Timing Chain/ Belt
-
Slipped Chain
- 🩺 Lack of Power | Incorrect Timing | Sprinter 906
-
📝 P0017 | Incorrect Timing | 2014 Subaru Impreza 2.0L
- P0017 Crankshaft/Camshaft ‘B’ System Correlation Bank 1. RH Exhaust VVT (bottom RH side of engine) was 8 degrees advanced on a scanner with ~10% duty cycle. LH Exhaust VVT was 0 degrees with ~10% duty cycle. Disconnecting VVT solenoid gave different code. Eliminated wiring issues. Turned out that exhaust camshaft RH was 1 tooth off.
- 📎 Engine Cutting Out | Incorrect Timing | Audi A6
-
📝 P0341. Incorrect Timing | 2006 Audi A6 3.2L
- P0341 Camshaft Position Sensor (G40): Implausible signal. Chain jumped a few teeth
-
📝 P0340 | Incorrect Timing | 2017 Ford Cmax
- P0340 – Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
- Note. If timing is even a little incorrect, it will trigger this code.
- Description doesn’t mention timing issues.
- 🩺 Lack Of Power, High Compression | Exhaust Camshaft Timing | VW Polo
-
Chain Guides, Tensioner
Wrong crankshaft
-
📝 Misfire cyl. 5 & 6. P0336. Wrong Camshaft. 2001 Chevy Camaro 5.7L
- P0336 CKP sensor range/performance. Misfires on cyl. #5 and #6.
- Crankshaft variation relearn cannot be completed.
- Waveform looks good, but it turned out that the wrong crankshaft was installed. There are two different 24X and 58X crankshafts reflectors that will fit this platform.
Crankshaft Position Relearn
- CKP variation relearn is only there for misfire diagnosis.
-
Crankshaft Position Relearn (P1336)
- P1336 Cadillac – Crankshaft Position System Variation Not Learned
- CKP variation relearn is only there for misfire diagnosis.
- Relearn Procedure (GM)
- Clear all codes.
Might need to apply parking brake and push on brake pedal before starting the car.
When you initiate the relearn, you have to steadily raise the RPM to above 4000 (within a 10 second period).
As soon as the RPM is high enough you will get a sharp stumble for a moment… immediately release the throttle and let the engine spin down to idle, turn key off and wait at least 15 seconds.
- Clear all codes.